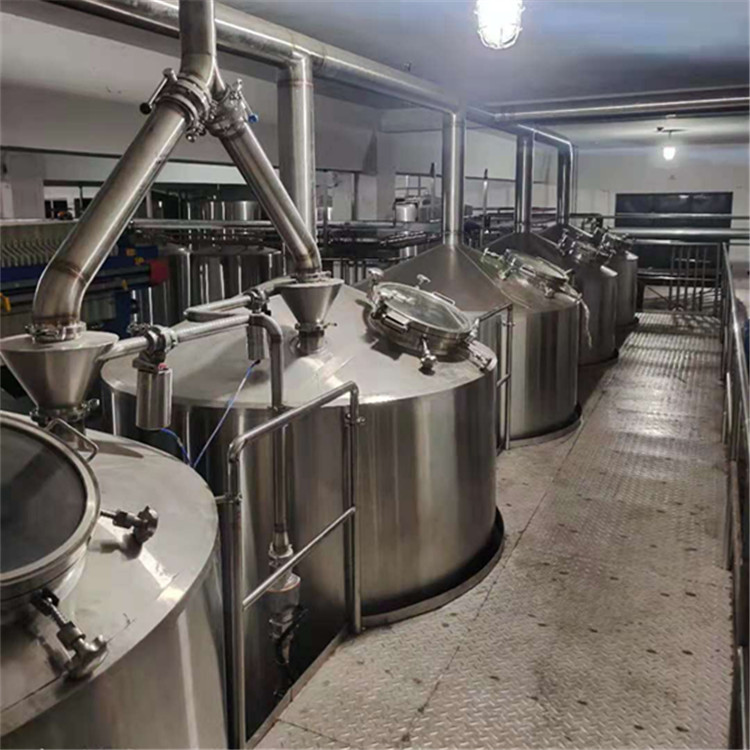

Different manufacturers have different requirements for beer equipment, different occasions, different configurations and different prices. No matter how large the beer equipment is, the principle of brewing beer is the same. Malt crushing - saccharification - Filtration - boiling - rotary sedimentation - cooling - Fermentation - bottling, so the whole beer system includes malt crushing system, saccharification system, fermentation system, refrigeration system, steam system, control system, filtration system, cleaning system, water treatment system, etc.
As we all know, beer is made of water, malt, hops and yeast. Therefore, the first step of brewing beer is malt crushing, which is divided into dry crushing and wet crushing. Generally, small and medium-sized beer equipment is equipped with double roll crusher, and large beer equipment has four or five rolls. Dry powder is generally used for small and medium-sized beer equipment, and wet powder is used for large beer equipment.
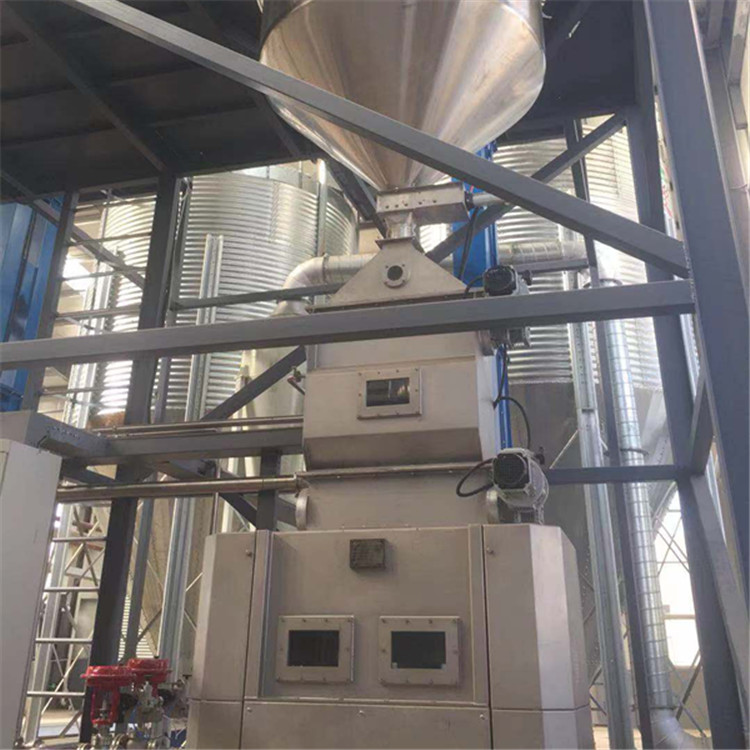

The above picture is wet crusher with weighing silo,It is suitable for beer equipment with large output. Wet crushing method can reduce the flying of malt dust and protect the production environment.
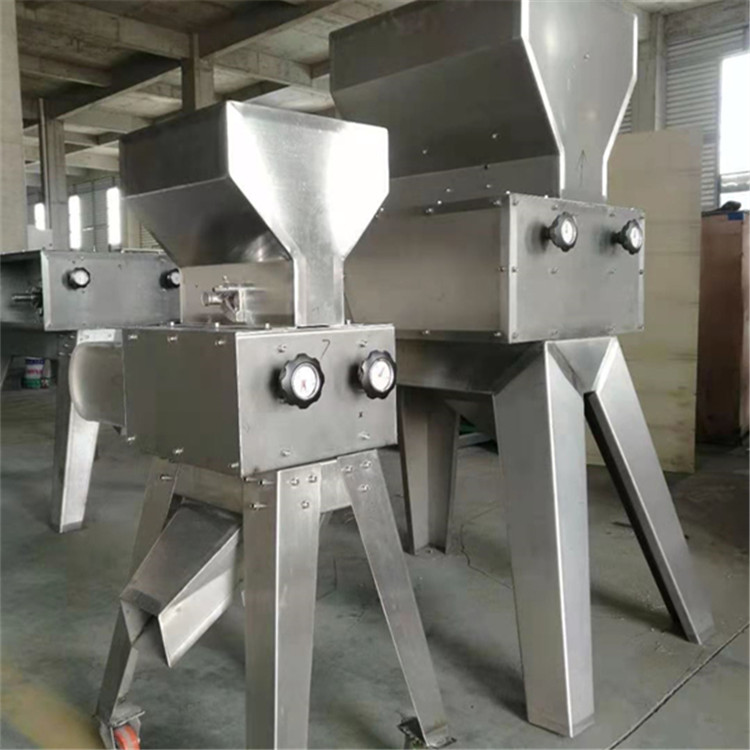

The above picture shows the dry powder crushing method, which is suitable for small and medium-sized beer equipment. It is recommended to use this method with small output, small floor area and cost saving.
After malt crushing, it is the most important step in the whole beer brewing - saccharification. The saccharification system, like the heart of the human body, is not only the core of beer brewing, but also a very key step. The saccharification system is divided into four steps: saccharification - lautering - boiling - whirlpool.
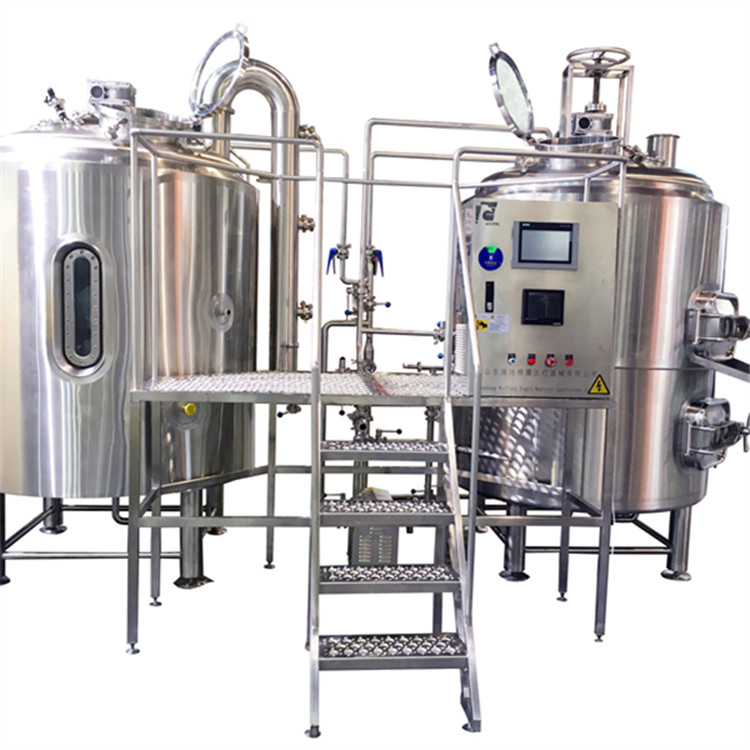

The first step:Mashing
There are one-step saccharification and multi-step saccharification. According to different brewed beer, the saccharification methods are also different. The following saccharification methods are for reference only.
One step saccharification:
Put 65 ℃ - 70 ℃ hot water into the saccharification pot, turn on the mixing, and slowly pour the crushed malt into the pot to make the mixing free of caking. Dissolve the starch in malt into sugar that can be stirred.
1. Put 37 ℃ water into the saccharification pot and soak it for half an hour to decompose the organic acids in the wort.
2. When the temperature rises to 45 ℃, protease can achieve moderate decomposition, and the decomposed amino nitrogen provides nitrogen source for yeast fermentation.
3. Heating at 65 ℃ can convert starch into sugar and provide carbon source for yeast.
4. When the temperature rises to 70 ℃, starch becomes dextrin, which is the colloidal substance of beer.
5. Raise the temperature to 78 ℃, inactivate the enzyme and finish saccharification.
The second step:lautering
Put 70 ℃ water into the filter tank to prevent the temperature of wheat mash from decreasing due to too cooling and reduce the filtration speed. Put the saccharified mash into the filter tank, open the ploughing knife until the mash is flat, stop the ploughing knife, open the reflux device for reflux until the wort is clear, close the reflux and put it into the boiling pot.
When washing the grains, inject hot water and repeat the above process until the grains are cleaned.
The third step:boiling
Boiling for about 1 hour is to kill all microorganisms and bacteria in wort, put them into hops, and boil the ascetic substances in hops to increase aroma.
Final step: whirlpool
Drive it into the whirlpool tank, stand still for 40 minutes, and then enter the plate heat exchanger for cooling, and the temperature will reach about 8 ℃.
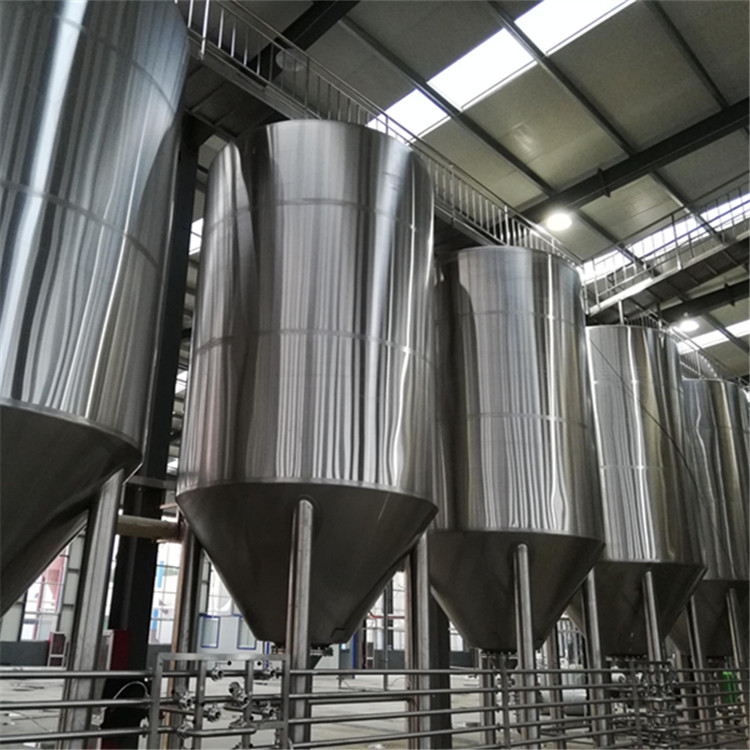

Fermentation is to convert the sugar in wort into alcohol and carbon dioxide through yeast. Generally, it is fermented for about 12-20 days, and different beer fermentation times are also different. The fermentation tank is cylindrical with conical bottom below, which is convenient for yeast precipitation, and yeast can be recovered for the next fermentation.
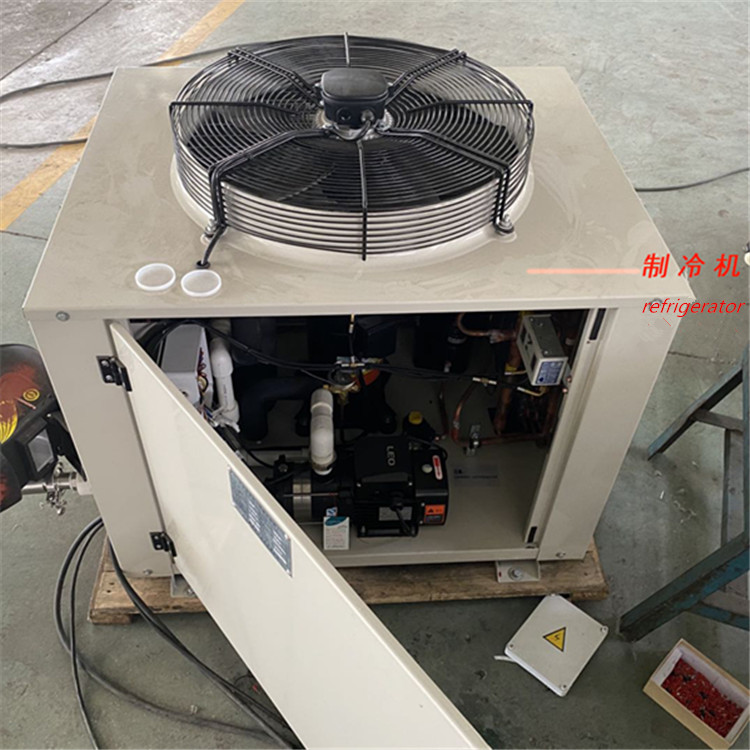
The refrigerator is used to cool the wort and fermentation tank after spin sedimentation.
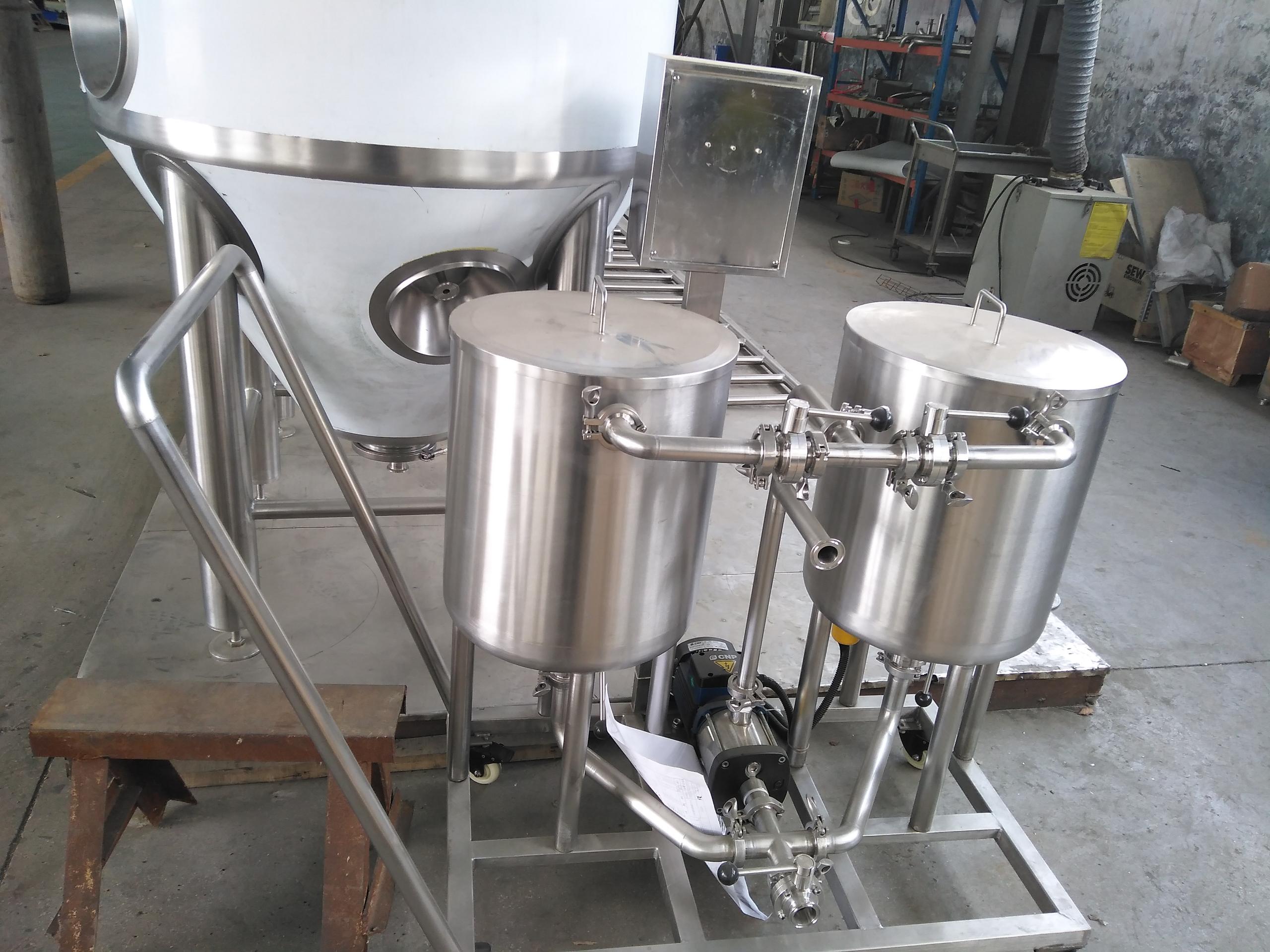

Breweries generally use cleaning in place (CIP) to clean and sterilize the equipment, that is, the process of cleaning and disinfecting the equipment without dismantling equipment parts or pipe fittings in a closed environment. The larger the equipment, the higher the requirements for cleaning the equipment. Configure CIP equipment according to equipment size and requirements.

It mainly refers to the electronic control, semi-automatic and automatic control of each system. Control of saccharification system, fermentation system, refrigeration system, etc. The control of small equipment is relatively simple and the price is relatively cheap. Large equipment has high control requirements, high automation level and complexity, and high cost.
| Code | Name | No. | Component |
| 1 | Malt milling system | 1 | Malt milling machine |
| 2 | Mash system | 1 | Mash/kettle tun |
| 2 | Lauter/whirlpool tun | ||
| 3 | Hot liquor tank | ||
| 4 | Plate heat exchanger | ||
| 5 | Wort oxygenator | ||
| 6 | Yeast addition tank | ||
| 7 | Operation platform | ||
| 8 | Wort pump | ||
| 9 | Hot water pump | ||
| 3 | Fermentation system | 1 | Fermenter |
| 2 | Mixing tank | ||
| 3 | PRV | ||
| 4 | Vent valve | ||
| 4 | Cleaning system | 1 | Mobile cleaning cart |
| 5 | Cooling system | 1 | Chiller |
| 2 | Glycol water tank | ||
| 3 | Ice water pump | ||
| 6 | Electrical System | 1 | Fermentation auto control |
| 2 | Switchboard | ||
| 3 | Fermentation control solenoid valve | ||
| 4 | Temperature Sensor | ||
| 5 | Wire and Cable | ||
| 6 | Threading tube | ||
| 7 | Filling system | 1 | Bottle rinsing machine |
| 2 | Linear filling and capping machine | ||
| 3 | Linear sticker labeling machine | ||
| 4 | Conveyor system | ||
| 8 | Steam system | 1 | Electric steam boiler |
| 9 | Pipeline accessories | 1 | Mash, CIP, water pipeline |
| 2 | Glycol water pipeline | ||
| 3 | Steam pipeline | ||
| 4 | Air compression pipeline | ||
| 5 | Food grade hose | ||
| 6 | Other |
If you want to ask anything just fill in the form below and send us.